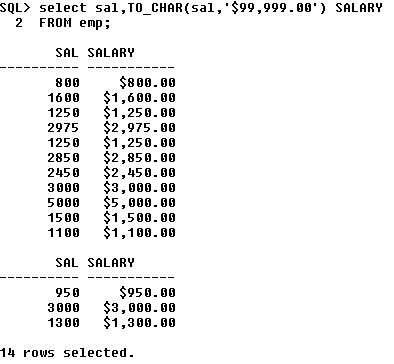
In some cases, Oracle server uses data of one data type where it expects data of a different data type. When this happens, Oracle server can automatically convert the data to the expected data type. This data type conversion can be done implicitly by Oracle server, or explicitly by the user.
Implicit Data Type Conversion
For assignments, the Oracle server can automatically convert the following:
From To
VARCHAR2 OR CHAR NUMBER
VARCHAR2 OR CHAR DATE
NUMBER VARCHAR2
DATE VARCHAR2
The assignment succeed if the Oracle server can convert the data type of the value used in the assignment to that of the assignment target.
Explicit data type conversion covers in Next post.